In the realm of safety gear, hard hats are essential for preventing head injuries and shielding against electrical hazards. These vital pieces of personal protective equipment (PPE) are indispensable across various industries, particularly in construction and electrical work, where the risk of head injury and electrical shock is significant.
Understanding Hard Hat Classes
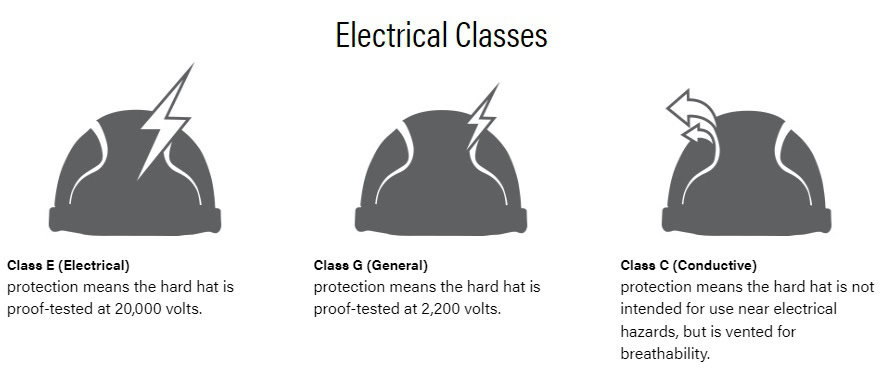
Hard hats come with a classification system that ensures they meet safety standards. The ANSI/ISEA Z89.1 standard categorizes hard hats into specific classes to address different types of hazards. Compliance with these standards is crucial for ensuring effective protection.
Types of Hard Hats
- Type I: Designed to protect against top impacts. Ideal for environments where the risk of falling objects is high.
- Type II: Provides protection against both lateral and top impacts, offering a higher level of safety for workers in environments with potential side impacts.
Electrical Classes of Hard Hats
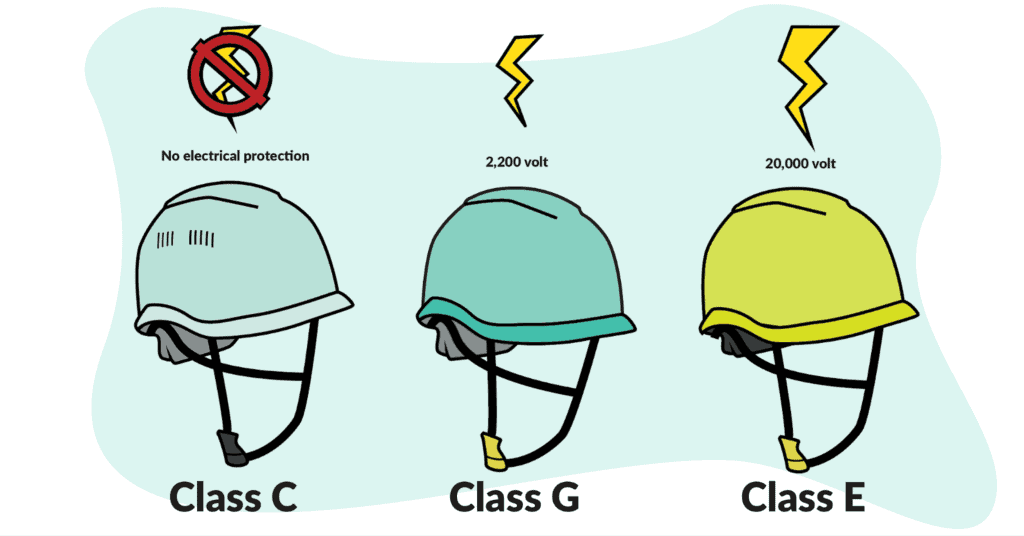
- Class E (Electrical):
- Protection: Provides high voltage protection up to 20,000 volts.
- Recommended For: Utility workers and electricians who work in high voltage environments.
- Features and Benefits: Offers superior dielectric protection and is built to withstand significant electrical hazards.
- Class G (General):
- Protection: Designed for low voltage protection up to 2,200 volts.
- Suitable For: General use in environments with some electrical hazards, but not for high voltage scenarios.
- Features and Limitations: Provides basic electrical protection but is not suitable for high voltage situations.
- Class C (Conductive):
- Protection: Not designed for electrical protection.
- Features: Lightweight and comfortable, ideal for environments where electrical hazards are not present.
- Use Cases: Best for areas where electrical hazards are minimal or non-existent.
Choosing the Right Hard Hat for Electrical Work
When selecting a hard hat, consider the following factors:
- Type of Electrical Work: Ensure the hard hat class matches the voltage and type of electrical work being performed.
- Environmental Conditions: Consider if the environment is wet or dry, as this can affect the hard hat’s performance.
- Fit and Comfort: Opt for a hard hat that provides a secure fit and comfort for extended wear.

Safety Standards and Compliance
OSHA regulations mandate the use of hard hats in environments where head injuries or electrical hazards are a risk. Regular inspection and maintenance of hard hats are essential to ensure they meet safety standards and provide the necessary protection.
Conclusion
Choosing the correct class of hard hat is crucial for protecting against electrical shock and other hazards. Adhering to safety standards and receiving proper training in PPE use are key to maintaining safety on the job. Ensure you select a hard hat that suits your specific work environment and electrical risk to stay safe and secure.











